WebQuest
Parts of Plants
Process

THE PLANT
Plants are living organisms that cover much of the land of planet Earth. You see them everywhere. They include grass, trees, flowers, bushes, ferns, mosses, and more. Plants are members of the kingdom plantae.
Plants have two Organ Systems: the shoot system and the root system.
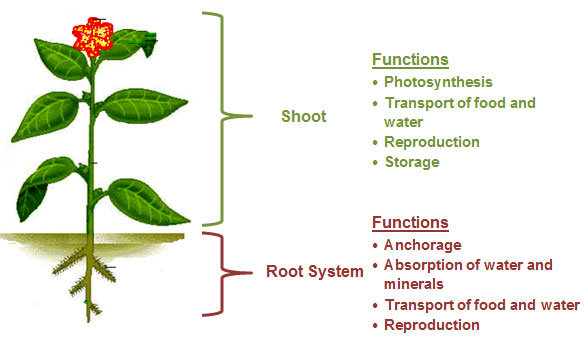
The root system is below ground. This system includes roots.
The shoot system is above ground. This system includes these organs: stems, leaves, and flowers.
There are million different kinds of plants, but, there are several things about them that are alike. Let’s look at some of the ways plants are alike:
Plants start from seeds (most of them)
Plants have roots
Plants have stems
Plants have leaves
Plants need soil, sun and water to live
Plants make their own food (photosynthesis)
All plants give us oxygen
The children will be given a YouTube audio visual to watch on the parts of a plant and their function.
We will be zooming in closer to the different parts of the plants ant there specific function, we will start from the bottom up to the top.
THE ROOT
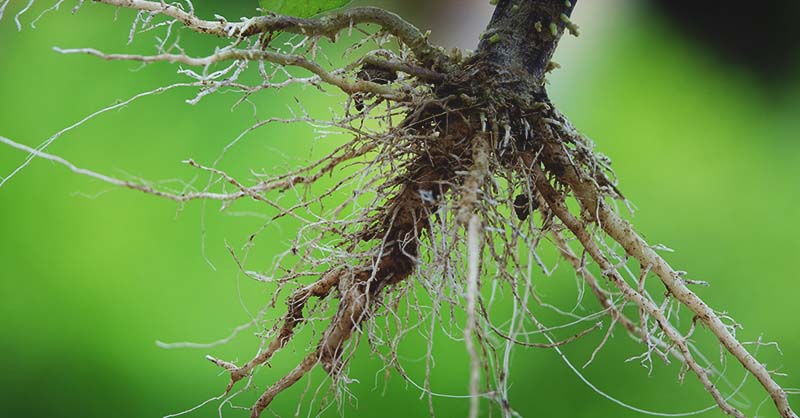

Roots are the important underground part of all vascular plants. This part of the plant is mainly responsible for anchoring it down into the ground and absorbing the essential mineral elements, nutrients, and water from the soil. It is also used to store food.
However, not all plants have their roots underground, some plants have their roots growing above the ground. These are called aerial roots. Alike underground roots, these aerial roots are also responsible for absorbing nutrients, anchoring and affixing the plant by supporting them to the structures such as nearby walls, rocks and trellises.
THE STEM

The stem of a plant is one of two structural parts of a vascular plant (a plant that has tissues for moving water and nutrients), the other being the root. The stem is the part above ground which provides support for leaves and buds. It's like the major highway of a plant, and it's vital for plant life. Nodes are the places on a stem where leaves and buds are found (the exits or intersections), and internodes are the areas in between nodes.
THE LEAVES
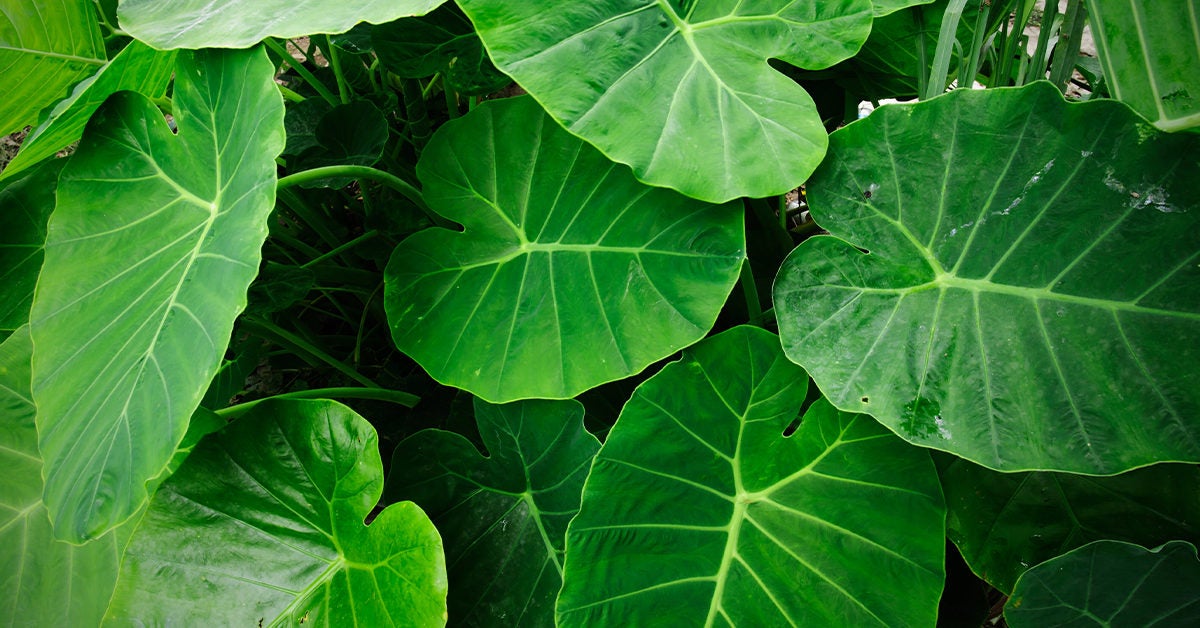

Leaf, in botany, any usually flattened green outgrowth from the stem of a vascular plant. As the primary sites of photosynthesis, leaves manufacture food for plants, which in turn ultimately nourish and sustain all land animals. Botanically, leaves are an integral part of the stem system. They are attached by a continuous vascular system to the rest of the plant so that free exchange of nutrients, water, and end products of photosynthesis (oxygen and carbohydrates in particular) can be carried to its various parts.
The main function of a leaf is to produce food for the plant by photosynthesis. Chlorophyll, the substance that gives plants their characteristic green colour, absorbs light energy. The internal structure of the leaf is protected by the leaf epidermis, which is continuous with the stem epidermis.
THE FLOWER
They help in reproduction, but they also provide nourishment for other living things. They produce a lot of nectar. There are complete or incomplete flowers in nature. The sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils make up a complete flower. On the other hand, an incomplete flower lacks one or more of these structures. A whole flower has two distinct parts: The Vegetative Part and Part of Reproduction. We’ve covered everything there is to know about reproduction in flowering plants in this post.
THE FRUIT
A fruit is a mature, ripened ovary, along with the contents of the ovary. The ovary is the ovule-bearing reproductive structure in the plant flower. The ovary serves to enclose and protect the ovules, from the youngest stages of flower development until the ovules become fertilized and turn into seeds. Eventually, the fruit functions to spread the seeds or to attract dispersers. There are many different kinds of fruit–from dry to fleshy, from dehiscent (splitting open) to indehiscent and from single seed to many-seeded.
The Public URL for this WebQuest:
http://zunal.com/webquest.php?w=775435
WebQuest Hits: 392
Save WebQuest as PDF
